Deploy Prometheus
Deploy Prometheus
First we are going to install Prometheus. In this example, we are primarily going to use the standard configuration, but we do override the storage class. We will use gp2 EBS volumes for simplicity and demonstration purpose. When deploying in production, you would use io1 volumes with desired IOPS and increase the default storage size in the manifests to get better performance. Run the following command:
kubectl create namespace prometheus
helm install stable/prometheus \
--name prometheus \
--namespace prometheus \
--set alertmanager.persistentVolume.storageClass="gp2" \
--set server.persistentVolume.storageClass="gp2"
Make note of the prometheus endpoint in helm response (you will need this later). It should look similar to below:
The Prometheus server can be accessed via port 80 on the following DNS name from within your cluster:
prometheus-server.prometheus.svc.cluster.local
Check if Prometheus components deployed as expected
kubectl get all -n prometheus
You should see response similar to below. They should all be Ready and Available
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/prometheus-alertmanager-77cfdf85db-s9p48 2/2 Running 0 1m
pod/prometheus-kube-state-metrics-74d5c694c7-vqtjd 1/1 Running 0 1m
pod/prometheus-node-exporter-6dhpw 1/1 Running 0 1m
pod/prometheus-node-exporter-nrfkn 1/1 Running 0 1m
pod/prometheus-node-exporter-rtrm8 1/1 Running 0 1m
pod/prometheus-pushgateway-d5fdc4f5b-dbmrg 1/1 Running 0 1m
pod/prometheus-server-6d665b876-dsmh9 2/2 Running 0 1m
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/prometheus-alertmanager ClusterIP 10.100.89.154 <none> 80/TCP 1m
service/prometheus-kube-state-metrics ClusterIP None <none> 80/TCP 1m
service/prometheus-node-exporter ClusterIP None <none> 9100/TCP 1m
service/prometheus-pushgateway ClusterIP 10.100.136.143 <none> 9091/TCP 1m
service/prometheus-server ClusterIP 10.100.151.245 <none> 80/TCP 1m
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE NODE SELECTOR AGE
daemonset.apps/prometheus-node-exporter 3 3 3 3 3 <none> 1m
NAME DESIRED CURRENT UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/prometheus-alertmanager 1 1 1 1 1m
deployment.apps/prometheus-kube-state-metrics 1 1 1 1 1m
deployment.apps/prometheus-pushgateway 1 1 1 1 1m
deployment.apps/prometheus-server 1 1 1 1 1m
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/prometheus-alertmanager-77cfdf85db 1 1 1 1m
replicaset.apps/prometheus-kube-state-metrics-74d5c694c7 1 1 1 1m
replicaset.apps/prometheus-pushgateway-d5fdc4f5b 1 1 1 1m
replicaset.apps/prometheus-server-6d665b876 1 1 1 1m
In order to access the Prometheus server URL, we are going to use the kubectl port-forward command to access the application. In Cloud9, run:
kubectl port-forward -n prometheus deploy/prometheus-server 8080:9090
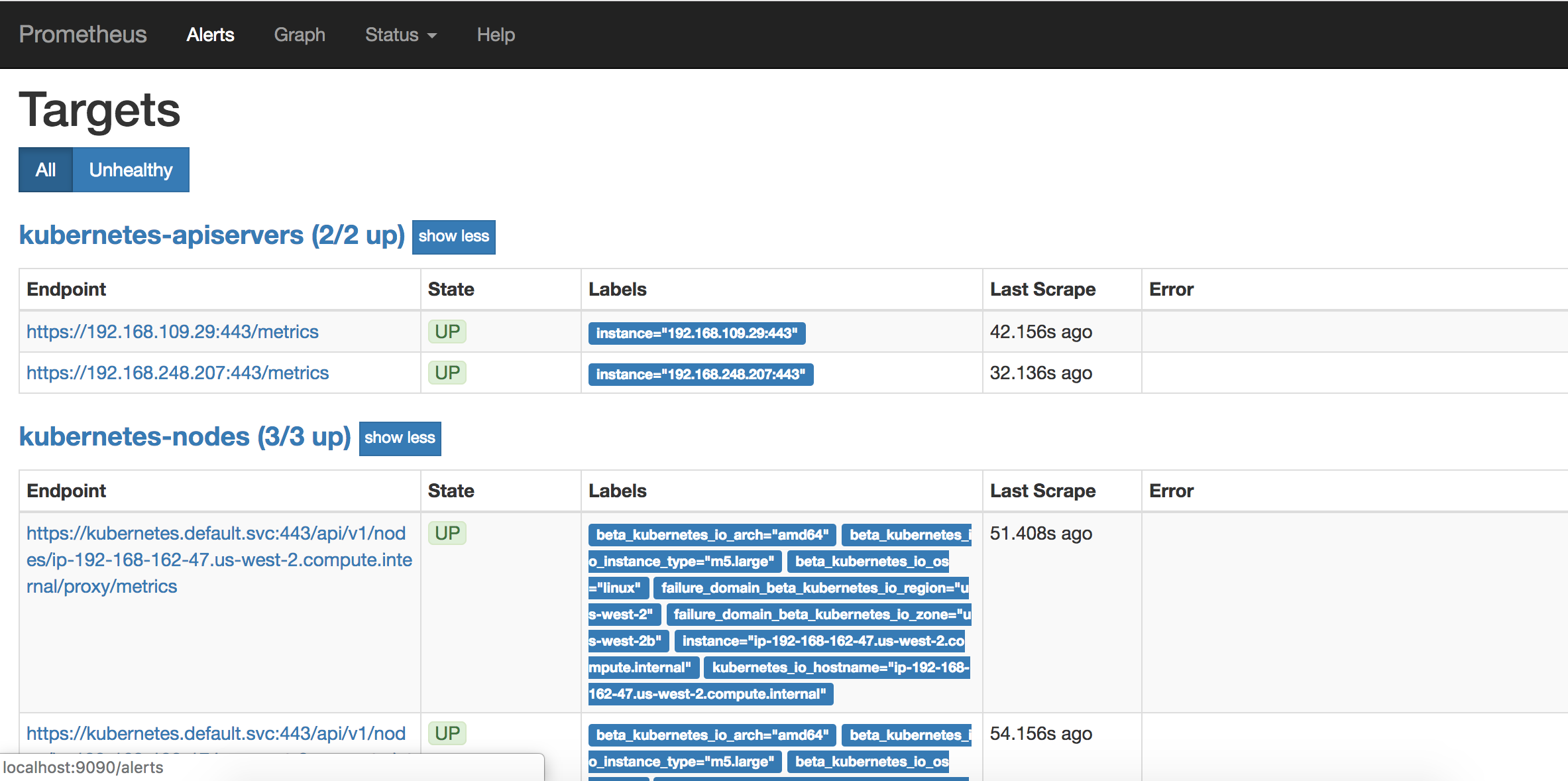
In your Cloud9 environment, click Tools / Preview / Preview Running Application. Scroll to the end of the URL and append:
/targets
In the web UI, you can see all the targets and metrics being monitored by Prometheus: